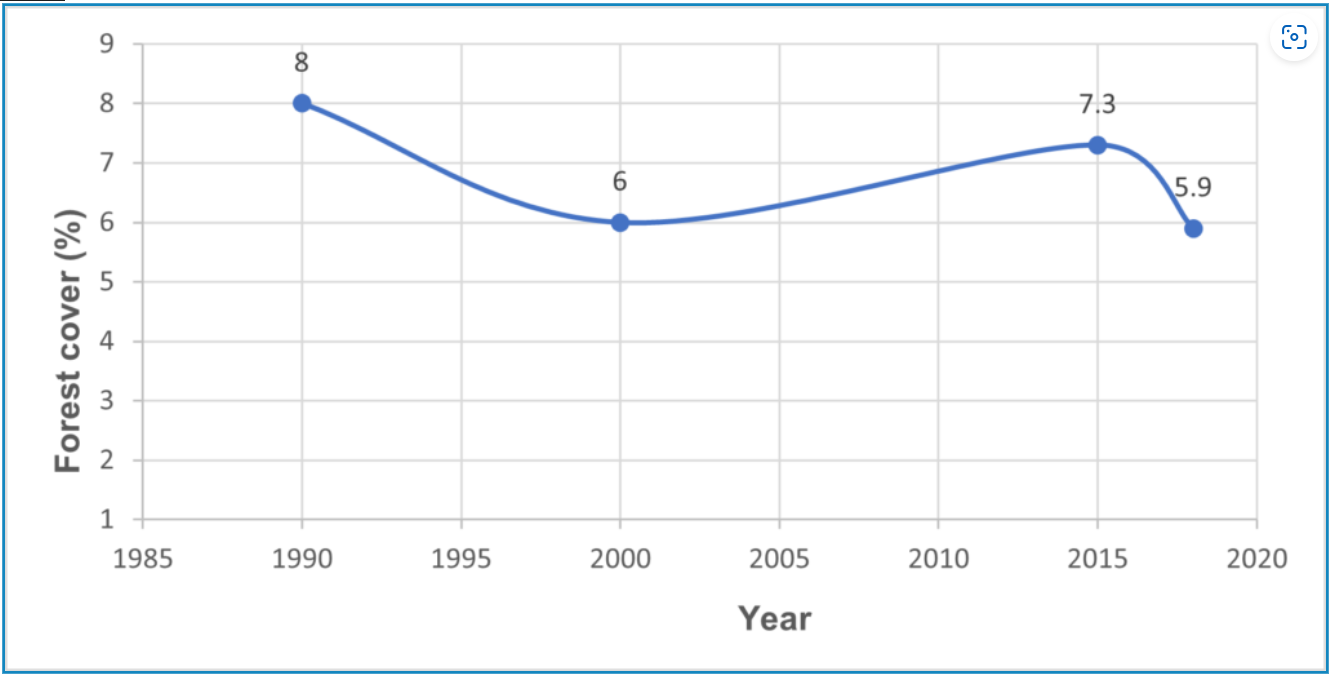
What is Intellectual Property?
According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) Intellectual Property (IP) is the creations of the mind such as inventions used in commerce. The difference between innovation and invention is that the former describes the process of translating an idea or invention into a good or service that creates value or which customers are willing to pay. An invention is a new scientific or technical idea and the means of its embodiment (source: business dictionary).
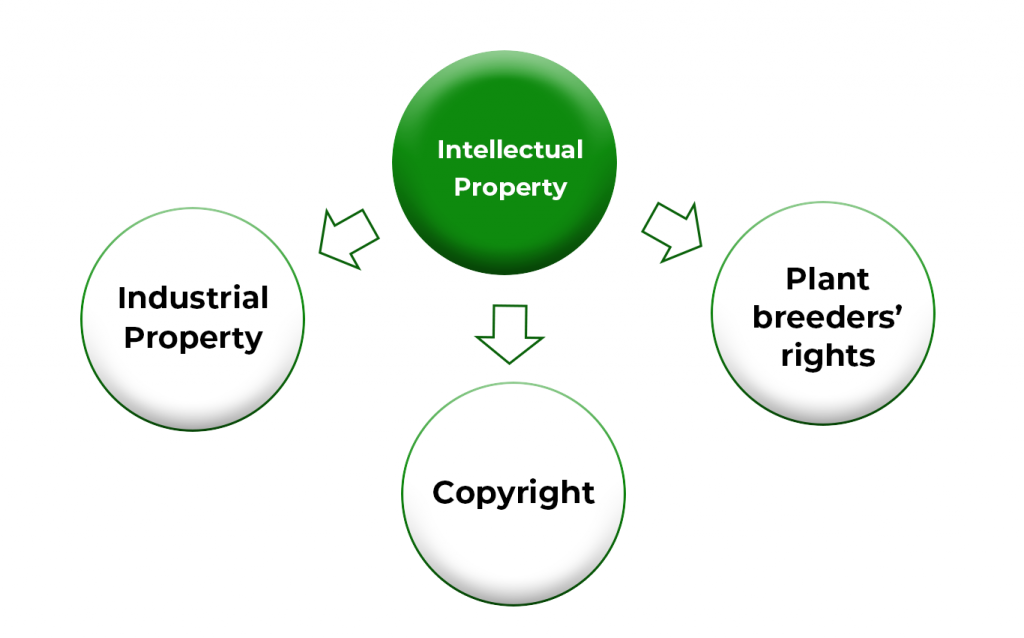
Intellectual Property is divided into three, namely; Industrial Property, Copyright and Plant Breeders Rights.
- Industrial Property is a form of intellectual property that relates to inventions and industrial designs. This includes trademarks, geographical indications, trade secrets, industrial designs, utility models and patents. A patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention.
- Copyright relates to literary and artistic work such as poems, novels, music, painting.
- Plant breeders’ rights is designed specifically to protect new varieties of plants. The rights include: production, selling, propagation.
Why go for protection?
Among the various reasons one should protect their Intellectual Property is to prevent or block competitors from duplicating your innovation, acquire transfer rights such as licensing and protect standards.
Information required to lodge a patent application
A patent application should be filed with the Kenya Industrial Property Institute consisting of:
- Completed request form
- Clear description of the invention
- One or more claims
- One or more drawings of the invention (where necessary)
- An abstract with the title and summary of technical details of the invention
- Deposit of micro-organism culture (where applicable)
Requirements for Patentability
Novelty, inventive step, and industrial applicability are the conditions for patentability. Exclusive rights give the patent owner the right to: control who makes, uses, sells, offers to sell and/or imports the patented invention. The owner can also seek injunction against infringement and claim damages for infringement.
What is disclosed in patent?
A patent should have some business information, that is the owner’s name and address, inventor’s name and address as well as potential partners’ details. Secondly, legal information such as the status of the patent application as well as patent claims is disclosed. Finally, some technical information namely background of the invention, summary of the invention, detailed description of the invention and method for carrying out the invention.
So, what can/cannot be patent?
| Patentable | Exclusions |
| Inventions Section 21 of the Kenya Industrial Property Act, inventions can be either/both a product (like machine) and process/method providing a solution to a specific problem in the field of technology. | Schemes, rules, and methods of doing business, performing purely mental acts, playing games, bank schemes, insurance, accounting, multilevel marketing, and merry-go-round |
| Biotechnological products or processes | Inventions contrary to public order, morality, public health, safety, environmental conservation |
| Plant varieties | |
| Discoveries, scientific theories, mathematical methods | |
| Mere presentation of information | |
| Methods of treatment of humans/animals by surgery or therapy |
Source; Presentation slides by Janet Kisio, KIPI